Do you know the difference between ionic and covalent bonding?
Covalent Bonding GCSE Quiz
Good Luck!
Covalent bonding occurs between non-metal elements such as hydrogen and oxygen. One or more electrons in the outermost shells are shared between atoms to complete the shells. Opposite charges attract and so the atoms are held together by their mutual attraction to the shared electrons since the overall charge of electrons is -1 and an atomic nucleus is +1.
We will use oxygen molecule covalent bonding as an example to help understand the concepts
Oxygen structure and the periodic table
Oxygen is a non-metal element in group 6 of the periodic table (sometimes written as group 16). This group number tells us that there are 6 electrons in the outermost electron shell. Also, remember that atoms are electrically neutral because the number of protons (+1 charge) and electrons (-1 charge) are equal. Learn more about atomic structure.
Remember, when two non-metals come together they form covalent bonds. Two metals would form a metallic bond and a metal and a non-metal would form an ionic bond.
Oxygen electronic structure explained with a dot and cross diagram
Oxygen has 6 electrons in its outermost shell. That means it needs two electrons to gain a complete outer shell.
Two oxygen atoms come together and form a double covalent bond by sharing their two electrons with each other. This creates a strong bond and oxygen molecules are more stable in this form than individual atoms. Oxygen is typically found in this form in the atmosphere due to this extra stability.
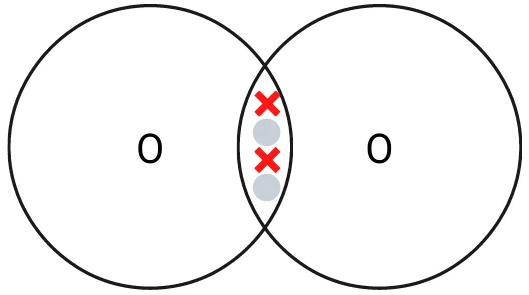
Covalent bonding of an oxygen molecule. Remember that many oxygen molecules are often present in the same area and weak intermolecular forces will hold them together.
Covalent Bonding Dot and Cross Diagram
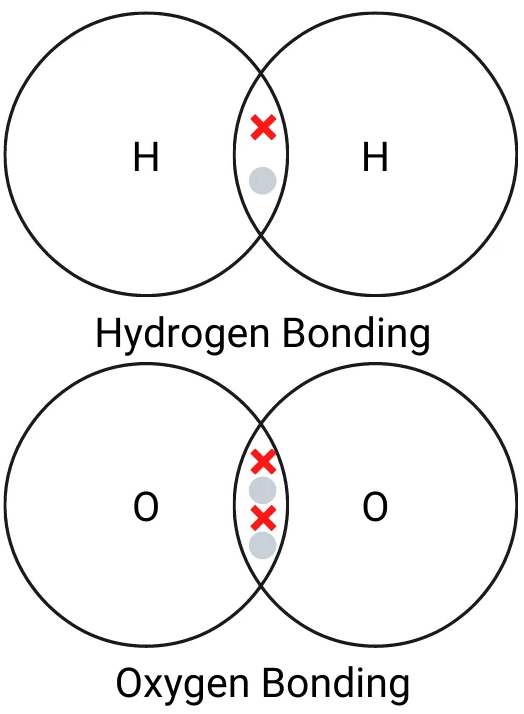
The dot and cross diagram below shows how covalent bonding works in hydrogen and oxygen. Remember, in an exam, they will want you to fill in the rest of the electrons in the outer shell, or perhaps in all of the shells.
Hydrogen has one electron in its outer shell. That means it needs one electron to form a bond. A hydrogen atom forms a single covalent bond, sharing one electron with another hydrogen atom.
Oxygen has 6 electrons in its outer shell. That means it needs two electrons to form a bond. An oxygen atom forms a double covalent bond, sharing two electrons with another oxygen atom.
Why is Diamond Hard?
Diamond is hard because each carbon atom has four strong covalent bonds with other carbon atoms, and they are arranged in a tetrahedral pattern which is also very strong.
Why does Graphite Conduct Electricity?
Graphite is made of carbon and each carbon atom has three covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Each carbon atom can form four covalent bonds meaning there is one delocalised electron that is free to carry a charge and since electrons have a charge of -1, graphite conducts electricity via the one free electron in each carbon atom.
Why is Graphite Soft and Slippery?
Graphite is soft because it is arranged in sheets of carbon atoms, but each sheet is only held together by weak intermolecular bonds. These weak bonds allow sheets of graphite to slide past each other, making graphite soft.
Why does Diamond and Graphite have a High Melting Point?
Both diamond and graphite have high melting points because they are held together by multiple covalent bonds. Each bond requires lots of energy to break and therefore lots of energy is needed to break all of the bonds between carbon atoms. These bonds must be broken in order to melt diamond and graphite, and so, diamond and graphite have high melting points.
How many Covalent Bonds will an Atom of Carbon Form with other Atoms?
Carbon can form 4 covalent bonds since it is in group 4 and it has 4 electrons in its outer shell. For atoms to be stable, they need a full outer shell which for carbon means it needs 8 electrons in its outer shell.
For more fundamental knowledge, check out the atomic structure quiz and the elements, compounds and mixtures quiz.
How many bonds can oxygen form?
Oxygen can form 1 double bond with another oxygen atom. This is where two electrons from each oxygen atom are shared with another oxygen atom. In total, this means that 4 electrons are shared.
