Do you know what the medulla is?
The Brain Quiz
This quiz is suitable for all exam boards and so it contains more information than you may be familiar with, but it’s worthwhile learning it all, especially if you are interested in doing A level Biology.
Parts of the brain and their functions
For your exam, you need to know the basic structures of the brain and their functions, as well as have an understanding of the difficulties of fixing brain injuries and treating disease.
Click on the tabs below to show more information about the brain.
Show Description
The cerebral cortex is the outer layer of the cerebrum, the largest part of the brain, and is responsible for higher-level functions such as thinking, reasoning, and decision-making, which are more developed in humans compared to simpler organisms.
The cerebrum is divided into two sections, known as the left and right hemispheres.
The cerebrum can also be divided into four sections, known as lobes, each of which has specific functions.
- Frontal lobe: Controls voluntary movements and is involved in decision-making, problem-solving, and planning.
- Parietal lobe: Processes and interprets sensory information such as touch, temperature, and pain.
- Temporal lobe: Involved in processing auditory information, visual memories, and language comprehension.
- Occipital lobe: Primarily responsible for processing visual information.
The cerebellum, located at the back of the brain underneath the cerebral hemispheres, is responsible for controlling and coordinating muscular movements. It helps the brain regulate balance, posture, and fine motor skills, enabling us to perform actions like walking and playing sports.
The medulla oblongata, located at the base of the brainstem above the spinal cord, is responsible for controlling vital unconscious functions that keep us alive. For example, it regulates heart rate and breathing rate. While you can breathe consciously, the medulla ensures that when you are sleeping, you continue to breathe automatically at the correct rate and depth, ensuring your body gets the oxygen it needs and removes excess carbon dioxide.
The hypothalamus, located deep within the brain, above the medulla and the pituitary gland, is responsible for producing and releasing important hormones. It serves as a crucial link between the nervous and endocrine systems. One of its major roles is maintaining homeostasis, which involves regulating internal body conditions such as temperature, hunger, and thirst within suitable ranges to keep us alive.
See Diagrams
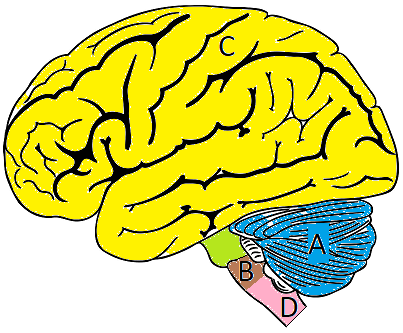
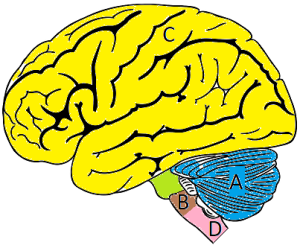
Diagram of the brain and spinal cord
- A – Cerebrum
- B – Medulla oblongata
- C – Cerebellum
- D – Spinal cord
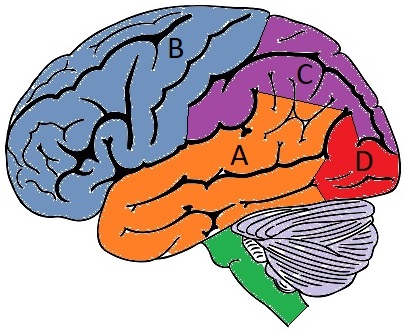
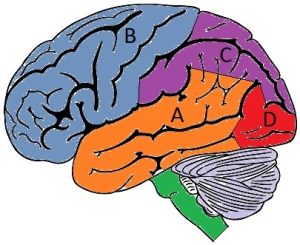
Diagram of the cerebral cortex
- A – Temporal lobe
- B – Frontal lobe
- C – Parietal lobe
- D – Occipital lobe