Mock test. 1 hour and 45 minutes. 100 marks available.
GCSE AQA Biology Paper 1
Good Luck!
Quiz Summary
0 of 61 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed this quiz. You cannot start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to take this quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Quiz complete. Results are being recorded.
Results
0 of 61 Questions answered correctly
Your Time:
Time has elapsed.
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
| Average Score |
|
| Your Score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 61Question 11 Point
Which sub-cellular structures can be found in animals?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 61Question 21 Point
The male gametes (sperm cells) are adapted to their function. Which of the following are adaptations of sperm cells?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 61Question 31 Point
Place the measurement units in order from biggest to smallest
- Micrometres (μm)
- Picometres (pm)
- Millimetres (mm)
- Kilometres (km)
- Metres (m)
- Nanometres (nm)
View Answers:
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 4 of 61Question 41 Point
Put the stages of the cell cycle in the correct order from start to finish
- Interphase
- Metaphase
- Cytokinesis
- Prophase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
View Answers:
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 5 of 61Question 51 Point
Which of the following are reasons why mitosis takes place?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 61Question 62 Points
Amidst, with, against
-
Complete the sentence: In diffusion and osmosis, particles move the concentration gradient, whilst in active transport, particles move the concentration gradient.
Correct 2 / 2 PointsIncorrect / 2 Points -
-
Question 7 of 61Question 71 Point
Which of the following are factors that affect the rate of diffusion?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 61Question 81 Point
Why does the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction increase with greater substrate concentration?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 61Question 91 Point
Why is the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction highest at an optimum pH?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 61Question 101 Point
Cardiac output is measured as the volume of blood pushed through the aorta each minute. Which is the correct equation for cardiac output?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 61Question 111 Point
The left ventricle has a thicker muscle wall, why is this the case?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 61Question 121 Point
What are the lower chambers of the heart called?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 61Question 131 Point
What is the role of coronary arteries?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 61Question 144 Points
Drag and drop to match the function to the correct part of blood
- Plasma
- White blood cells
- Red blood cells
- Platelets
- Carrying dissolved substances around the body
- Protecting the body from foreign cells
- Carrying oxygen around the body via haemoglobin
- Healing wounds by clotting the blood
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 61Question 151 Point
Which type of white blood cell engulfs (surrounds) foreign cells in order to digest them?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 61Question 162 Points
Which of the following features are found in veins?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 61Question 171 Point
Undernutrition, extranutrition, overnutrition, malnutrition
-
Complete the sentence: happens when you consume too little or too much of a particular nutrient.
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 18 of 61Question 181 Point
If coronary arteries are blocked, new blood vessels can be inserted, what is this procedure called?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 61Question 191 Point
What is the best way to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 61Question 202 Points
Companion, guard, root hair, translocation, transpiration
-
Complete the statement: During sucrose is transported in the sieve tubes of phloem vessels. cells pump sucrose across sieve cells up shoots or down to storage organs.
Correct 2 / 2 PointsIncorrect / 2 Points -
-
Question 21 of 61Question 213 Points
Phloem, xylem, guard cells, stream, stomata, root hair cells, hoses
-
Complete the statement: Water is pulled up the vessels as water evaporates from the vessels in the leaves. As the water vapour diffuses through the more water evaporates from the vessels. This creates a continuous chain of water called the transpiration .
Correct 3 / 3 PointsIncorrect / 3 Points -
-
Question 22 of 61Question 223 Points
-
Complete the sentence: The World Health Organisation (WHO) defines health as a state of complete , and well being.
Correct 3 / 3 PointsIncorrect / 3 PointsUse some of the following words:
mental
environmental
immune
social
physical
-
-
Question 23 of 61Question 231 Point
If left untreated, HIV will develop into which disease?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 61Question 241 Point
-
Complete the sentence. A is a disease-causing organism.
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 25 of 61Question 251 Point
How do antibiotics work?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 61Question 261 Point
If a person has a disease they may be more susceptible to another disease. Which of the following reasons could explain why this is true?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 61Question 271 Point
Place the following statements in the correct order:
- Other lymphocytes stay in the blood and as memory lymphocytes ready to attack the pathogen if it enters the body again)
- A pathogen enters the body and bypasses the physical and chemical defences
- Activated Lymphocytes divide to make clones
- The lymphocytes with antibodies that match the shape of the antigens on the pathogens are activated
- Some lymphocytes eject antibodies which stick to the antigens of pathogens and destroy them
View Answers:
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 28 of 61Question 281 Point
Which of the following are physical barriers stopping pathogens from entering the body?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 61Question 292 Points
What is the balanced chemical equation for photosynthesis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 61Question 301 Point
In which sub-cellular structure inside plant cells does photosynthesis occur?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 61Question 314 Points
Which of the following are the 4 factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 61Question 323 Points
Which of the following are 3 of the adaptations of leaves for efficient photosynthesis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 61Question 331 Point
Which of the following is the correct word equation for aerobic respiration?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 61Question 341 Point
Which system is responsible for ensuring the supply of oxygen and glucose to cells?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 61Question 351 Point
What is the purpose of respiration?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 61Question 361 Point
What is an advantage of anaerobic respiration?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 61Question 373 Points
Drag and drop to match the role and structure
- Cytoplasm
- Chloroplasts
- Mitochondria
- Supports and suspends structures within cells and where chemical reactions take place
- Where photosynthesis takes place
- Where aerobic respiration takes place
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 61Question 383 Points
Drag and drop to match the role and structure
- Ribosomes
- Cell wall
- Vacuole
- Sites of protein synthesis (where proteins are made)
- Supports the cell providing strength and flexibility for growth
- Stores nutrients and salts
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 61Question 391 Point
Xylem, phloem, guard cells, root hairs
-
Complete the sentence: living cells in use energy to transport sucrose around the plant.
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 40 of 61Question 401 Point
What is the role of physical barriers and chemical defences?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 61Question 412 Points
Which of the following are chemical defences against pathogens?
CorrectIncorrectLysozymes are enzymes found in tears and saliva which damage bacterial cell walls
-
Question 42 of 61Question 422 Points
Antigens, antibiotics, antibodies, lymphocytes, phagocytes
-
Complete the sentence:
White blood cells called have molecules on their surfaces called .
Correct 2 / 2 PointsIncorrect / 2 Points -
-
Question 43 of 61Question 431 Point
Which of the following types of pathogens can antibiotics be used on?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 44 of 61Question 445 Points
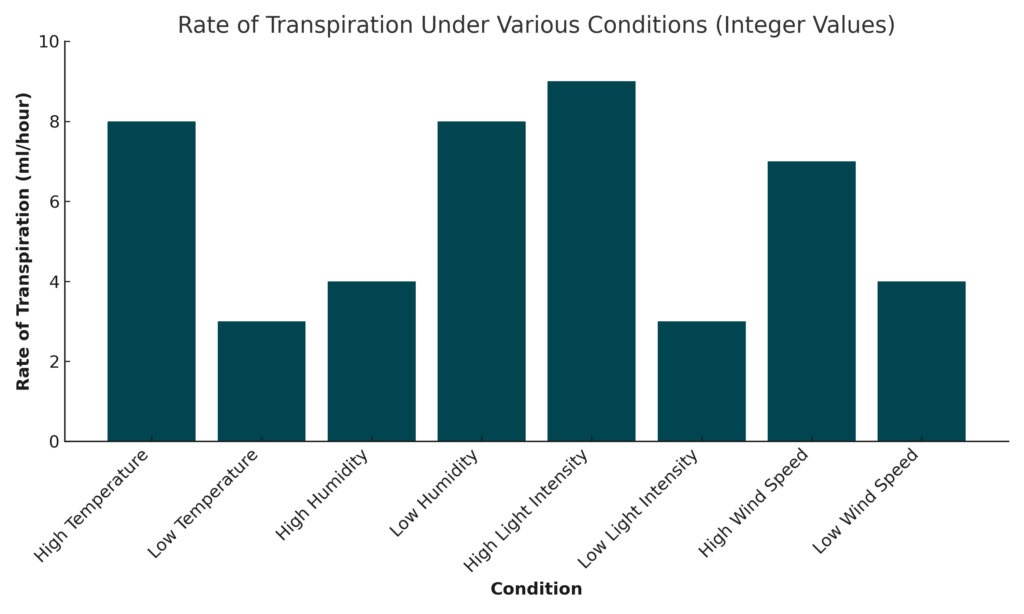
Look at the graph below:
Fill in the table below based on the graph.
-

Condition Rate of Transpiration (ml/hour) High Temperature 8 Low Temperature 4 Low Humidity 9 Low Light Intensity 3 High Wind Speed Low Wind Speed 4
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 45 of 61Question 453 Points
Match the structure of the brain with the correct function.
- Memories, language, consciousness, intellegence
- Muscular coordination
- homeostasis
- Cerebellum
- Cerebrum
- Hypothalamus
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 46 of 61Question 461 Point
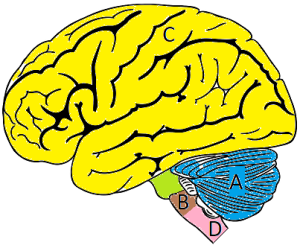
Look at the image of the brain and put the names of the structures in the correct order from A to D.

- Cerebellum
- Spinal cord
- Cerebrum (cerebral cortex)
- Medulla oblongata
View Answers:
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 47 of 61Question 474 Points
Which of the following are problems associated with treating brain injuries and disease?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 48 of 61Question 481 Point
Chaotic, controlled, peaceful, uncontrolled
-
Cancer cells form when changes in cells lead to cell division
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 49 of 61Question 491 Point
Marigolds, septioids, meristems, endocrines
-
Complete the sentence: Groups of cells in rapidly growing parts of plants, such as the roots and shoots have a special ability to turn into any kind of cell. These groups of cells are called .
CorrectIncorrectUse one of the following words:
Omnipotent cells
Meristems
Palisade
Xylem
-
-
Question 50 of 61Question 502 Points
Inactive, static, passive, effective, active
-
Complete the sentence: Diffusion and osmosis are processes whilst active transport is an process.
Correct 2 / 2 PointsIncorrect / 2 Points -
-
Question 51 of 61Question 511 Point
After digestion, the products are used to:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 52 of 61Question 521 Point
Arrange the following organs in the order in which food passes through them during digestion.
- Esophagus
- Mouth
- Small intestine
- Stomach
View Answers:
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 53 of 61Question 533 Points
Match the enzyme to its primary function.
- Breaks down starch to simple sugars (maltose)
- Breaks down proteins to amino acids
- Breaks down lipids to glycerol and fatty acids
- Amylase
- Protease
- Lipase
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 54 of 61Question 542 Points
Which of the following are functions of bile?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 55 of 61Question 553 Points
Drag and drop to match the disease with the mode of transmission
- Animal vectors
- Blood exchange/sexual contact
- Infected food
- Malaria
- HIV
- Salmonella
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 56 of 61Question 563 Points
Drag and drop to match the type of pathogen with the correct disease
- Viruses
- Bacteria
- Protists
- Measles and HIV
- Salmonella
- Malaria
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 57 of 61Question 571 Point
Which of the following is the source of energy that powers the metabolism?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 58 of 61Question 581 Point
Why does the heart rate, breathing rate and breath volume increase during exercise?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 59 of 61Question 591 Point
How is lactic acid removed by the body?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 60 of 61Question 601 Point
Antigens, antibiotics, antibodies
-
Complete the sentence: Pathogens have on their surface and the immune system uses them to tell if something has come from outside of the body.
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 61 of 61Question 611 Point
Use one of the following words to complete the sentence.
Directly, inversely, strictly, adversely
-
Light intensity is proportional to distance.
CorrectIncorrect -
Is this higher or foundation?
This is a combined paper for higher and foundation students. You can achieve grades 1 – 9 on this paper, so it is suitable for all. Grades are moderated against the average result to give the most accurate indication of your performance. You can look at – How is this paper marked? for more information.
How is this paper marked?
This paper is automatically marked to determine which questions were answered correctly.
Your grade is determined using a Z-Score moderation system. Your GCSE exams are also moderated comparably so that the difficulty of papers is taken into account.
Roughly, this works by calculating your overall percentage and comparing it to the average percentage and the standard deviation. This means that for harder papers you need fewer points to get the same grade as you would for an easier paper.
As more students attempt the paper, the average score and standard deviation more accurately represent the difficulty of the paper and the grades become more accurate.
Making these papers and the marking system took considerable effort so if you found them helpful for your revision, please show your appreciation by rating the page.
Which exam board are you studying?