GCSE Physics Equations
GCSE Physics Equations by Exam Board
This includes all major exam boards – AQA, Edexcel and OCR. There are some minor differences between exam boards and so you can access complete equation lists for each at the below links.
AQA Combined Science Trilogy/Synergy Physics Equations Sheet
AQA Physics Equations Sheet
Edexcel Combined Science Physics Equations Sheet
Edexcel Physics and Combined Science Physics Equations Sheet
OCR Combined Science Physics A Equation Sheet
OCR Combined Science B Equation Sheet
OCR Physics A Equation Sheet
OCR Physics B Equation Sheet
Complete list of all GCSE Physics Equations
Below is a complete list of all of the GCSE Physics Equations that you could need during your exams.
| Efficiency = useful power output / total power input | |
| Period = 1 / frequency | |
| Magnification = image height / object height | |
| Wave speed = frequency × wavelength | |
| Energy transferred = power × time | |
| Efficiency = useful energy transferred / total energy transferred | |
| Charge [flow] = current × time | |
| Potential difference = current × resistance | |
| Potential difference = work done (energy transferred) / charge [flow] | 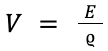 |
| Energy transferred (work done) = charge [flow] × potential difference | |
| Power = potential difference × current | |
| Power = (current)² × resistance | 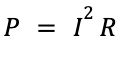 |
| HT force = magnetic flux density × current × length of conductor | |
| HT potential difference across primary coil × current in primary coil = potential difference across secondary coil × current in secondary coil | 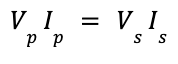 |
| HT potential difference across primary coil / potential difference across secondary coil = number of turns in a primary coil / number of turns in secondary coil | 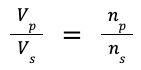 |
| Weight = mass × gravitational field strength | |
| Average speed = distance / time | 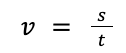 |
| Acceleration = change in speed / time taken | 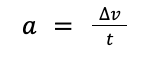 |
| (final speed)² – (initial speed)² = 2 × acceleration × distance |  |
| HT momentum = mass × velocity | |
| HT change in momentum = resultant force × time for which it acts | 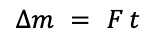 |
| Moment of a force = force × distance (normal to direction of the force) | |
| Force = mass × acceleration | |
| Work done = force × distance (along the line of action of the force) | |
| Kinetic energy = 0.5 × mass × (speed)² | 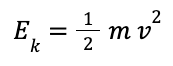 |
| Gravitational potential energy = mass × gravitational field strength × height | 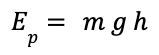 |
| Change in internal (thermal) energy = mass × specific heat capacity × change in temperature | 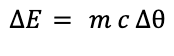 |
| Energy to cause a change of state = mass × specific latent heat | |
| Force exerted by a spring = extension × spring constant | |
| Energy stored in a stretched spring = 1/2 × spring constant × (extension)² | 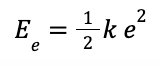 |
| Pressure = force normal to a surface / area of that surface | |
| For gases: pressure × volume = constant (for a given mass of gas and at a constant temperature) | |
| HT pressure due to a column of liquid = height of column × density of liquid × gravitational field strength | |
| Energy transferred = current × voltage × time | |
| Refractive index = sin(angle of incidence) / sin(angle of refraction) | 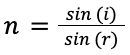 |
| Sin(critical angle) = 1 / refractive index | 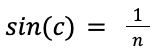 |
| Efficiency = useful energy output/total energy output x 100% | |
| Pressure / temperature = constant | 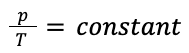 |
| Orbital speed = 2 x π x orbital radius / time period | 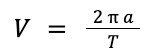 |
| Change in wavelength / reference wavelength = velocity of a galaxy / speed of light | 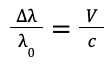 |
Ready to practise? Quickly select your past paper below!

