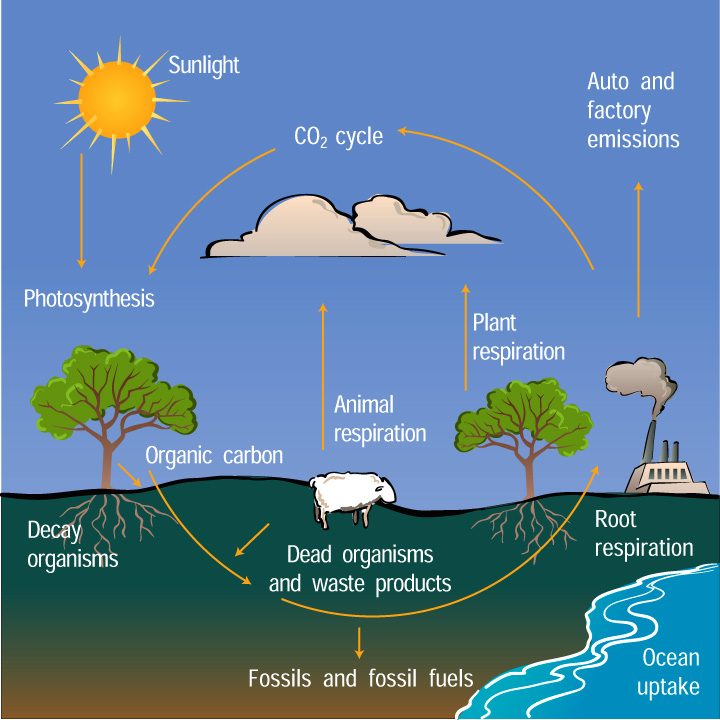
Just as with the water cycle and nitrogen cycle, carbon is cycled around the Earth through physical, chemical and biological stores. Trees and vegetation are perhaps where the cycle begins as they perform photosynthesis and take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere (or the water in the case of aquatic or marine plants) this is then turned into biomass and stored before being eaten by animals where it is moved into another temporary store.
Vegetation could be consumed whilst it is still alive or it could be consumed by organisms called decomposers after the plant dies. At these stages, carbon dioxide is produced through the breakdown of glucose during respiration and released back into the atmosphere.
Remember that these processes also happen in the oceans and remove carbon dioxide from the water. Photosynthesising organisms make glucose and this eventually ends up sinking to the bottom of the oceans. Layers and layers of dead organic matter build up over time and become part of the Earth’s crust, producing oil and gases and being locked away in rocks.
Learn more about where photosynthesis takes place in cells!