Do you know the difference between parasitism and mutualism?
Parasitism and Mutualism Quiz
We consider the ideas and concepts in this topic to be important for all to understand, although it is not covered by every exam board and course.
If your course is not included in the below list, you can skip this topic.
This topic is assessed by the following courses:
Edexcel Combined Science
Edexcel Biology (Separate Sciences)
OCR Combined Science A
OCR Biology A (Separate Sciences)
Good Luck!
What are parasitism and mutualism?
Parasitism and mutualism are examples of interactions between different species (interspecific). Remember that a community of organisms includes all of the species that live in an area.
Parasitism involves using another living organism for nutrition, usually keeping them alive in the process. This is a one-way relationship where only one individual benefits, at the expense of the other.
An interesting example of parasitism is vampire bats which feed on the blood of living animals.
Mutualism is where a partnership develops between individuals of different species where both individuals benefit.
Crocodiles having their teeth cleaned of leftover food by small birds is a great example of mutualism. The crocodiles are less likely to develop infections in their mouths from rotting meat and the birds are able to gain a meal.
Parasitism and mutualism are both examples of biotic factors. Other biotic factors include interactions between species such as competition and predation.
For GCSE you only need to know about competition, predation, parasitism and mutualism but to get a fuller picture of the interactions between species you must also consider commensalism and amensalism. See the table to understand the relative interactions between species and who wins, loses and draws.
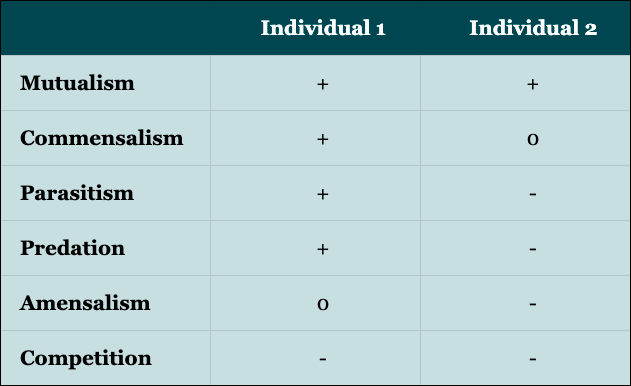
Visual demonstration of interspecific interactions within communities. + is gain, – is loss and 0 is neutral.
Commensalism is where one organism benefits at no expense to another e.g. a bird living in an existing hole in a tree, the bird causes no harm to the tree, but the bird gains shelter.
Amensalism is where an organism harms another, without gaining a benefit. Trampling of grasses by mammals is a typical example. Although, it could be argued that there is some benefit gained to the animal since it is able to transport itself.
As you can see by the table demonstrating the relative effects of the different interspecific interactions, competition is bad for both species. This is partially why evolution and behavioural changes drive species to occupy ecological niches that have the minimum possible overlap, to avoid competition.
We hope you enjoyed this quiz about parasitism and mutualism. Consider learning more about ecology with this quiz on sampling methods.
