Mock test. 1 hour and 45 minutes. 90 marks available.
Each time the test is taken it will present different questions.
Mock test. 1 hour and 45 minutes. 90 marks available.
Each time the test is taken it will present different questions.
Well Done you passed the test! You’re on your way to getting the grades you want!
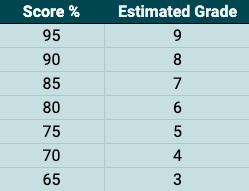
Why not try another Science Mock Exam and see how well you do?
Nice try, check your answers to see where you went wrong.

Why not get a bit more practice with some chemistry quizzes and then come back and have another try!
Select all that apply:
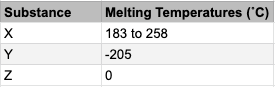
Select all that apply:
Select all that apply:
Neutralisation reactions follow the general structure –
metal oxide acid = salt water
the acid produces hydrogen ions and the metal oxide produces oxide ions – these combine to make the water
the salt is comprised of the remaining products – the metal and the other element from the acid
in this case, the other element is chlorine
The naming convention is to put the metal first for the salt created
Select all that apply:
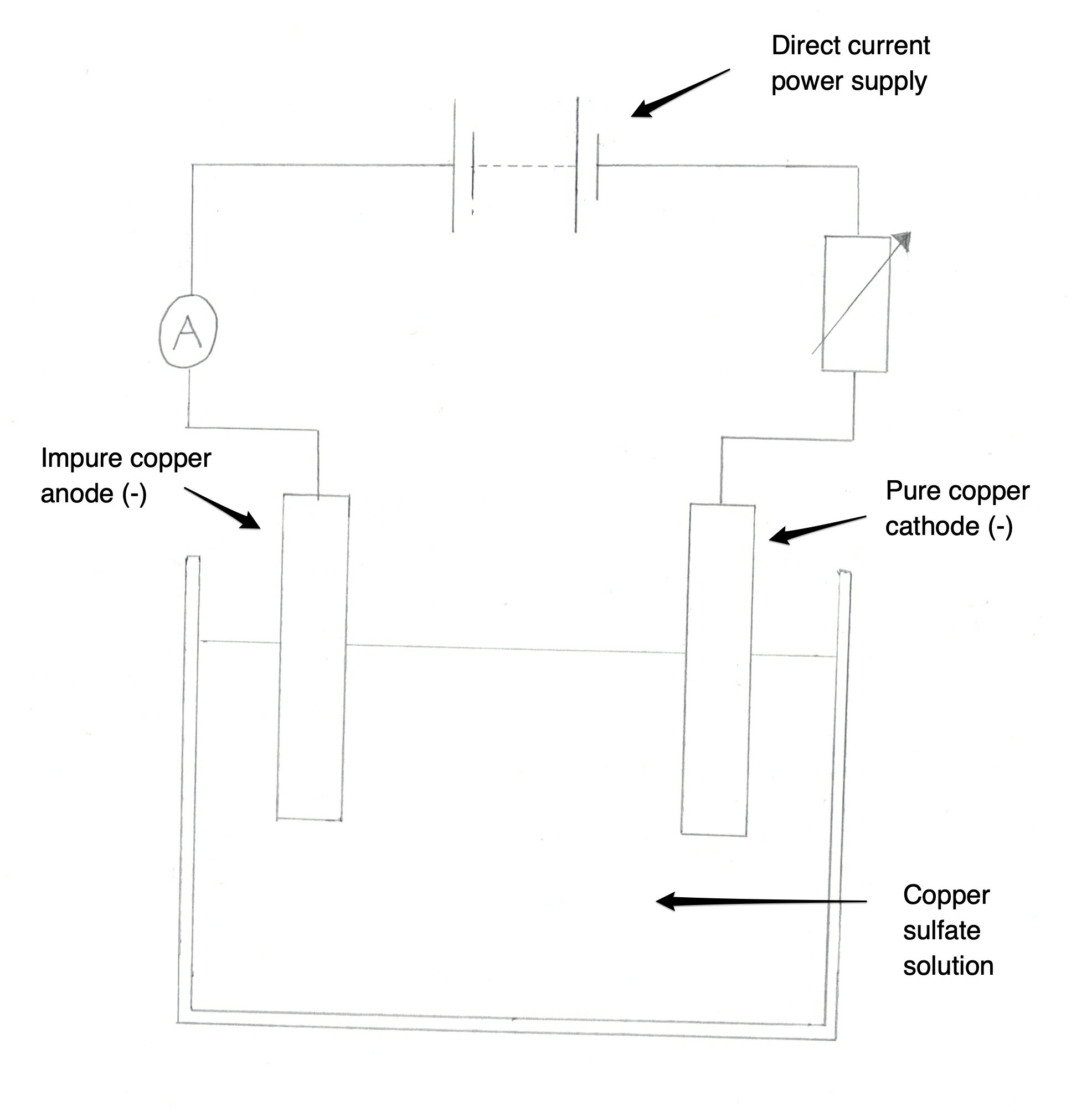
Select all that apply:

Select all that apply:
Select all that apply:

Select all that apply: