Mock test. 1 hour and 45 minutes. 90 marks available.
Each time the test is taken it will present different questions.
Mock test. 1 hour and 45 minutes. 90 marks available.
Each time the test is taken it will present different questions.
Well Done you passed the test! You’re on your way to getting the grades you want!
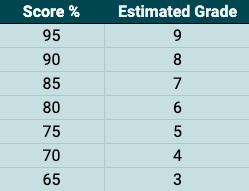
Why not try another Science Mock Exam and see how well you do?
Nice try, check your answers to see where you went wrong.

Why not get a bit more practice with some chemistry quizzes and then come back and have another try!
Select all that apply:
Select all that apply:
Select all that apply:
Select all that apply:
Select all that apply:
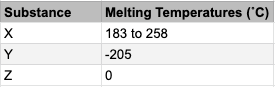
Remember:
acids produce an excess of hydrogen ions
alkalis produce an excess of hydroxide ions
hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions come together to make water which is neutral.
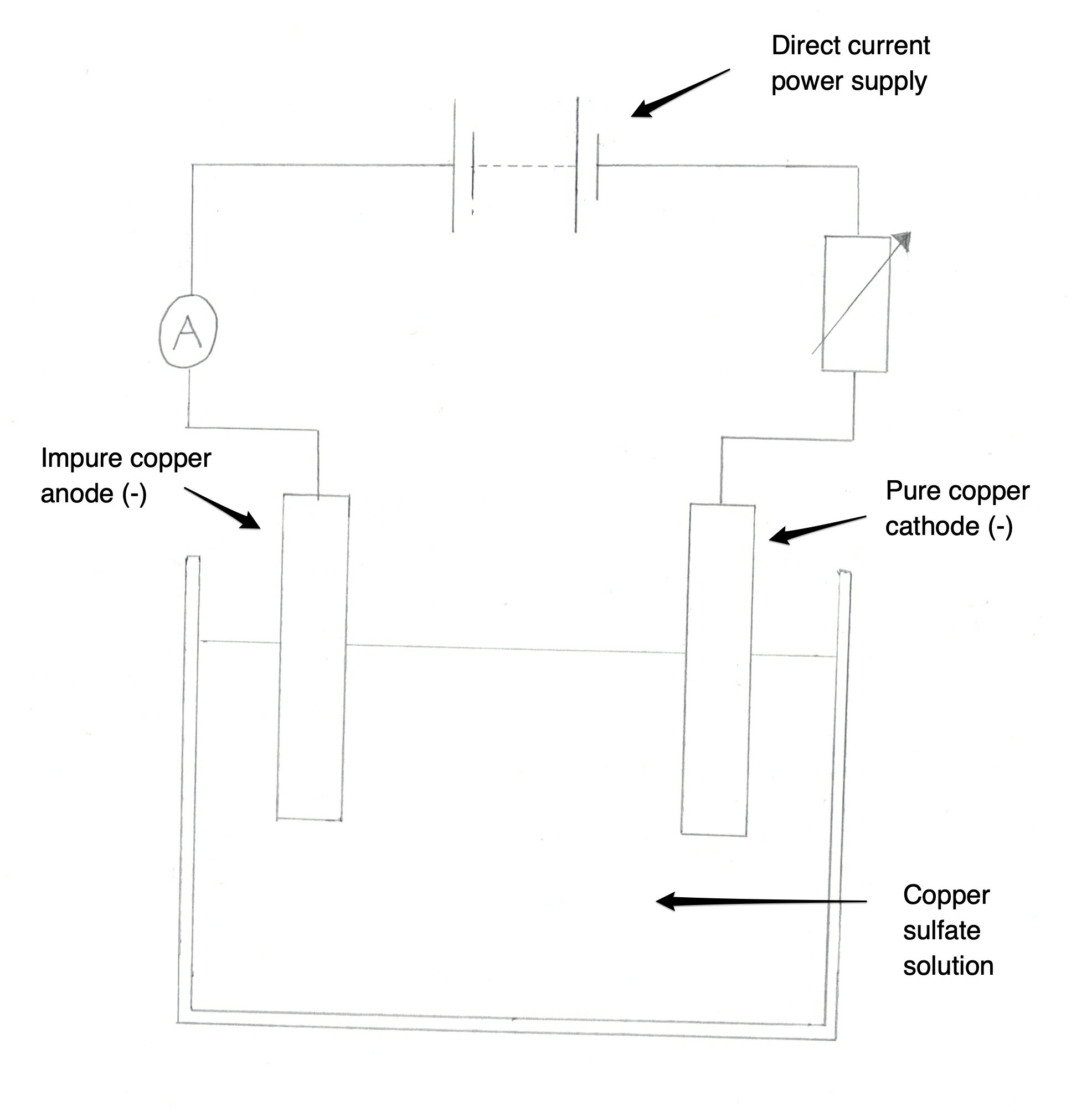
Select all that apply:
Select all that apply:
Remember to carefully read the question, if you selected Root hair cells, you were mistaken because the question asked about leaves, not roots.
