Mock test. 1 hour and 45 minutes. 90 marks available.
Each time the test is taken it will present different questions.
Mock test. 1 hour and 45 minutes. 90 marks available.
Each time the test is taken it will present different questions.
Well Done you passed the test! You’re on your way to getting the grades you want!
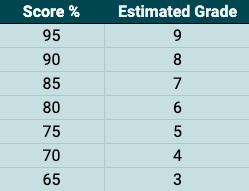
Why not try another Science Mock Exam and see how well you do?
Nice try, check your answers to see where you went wrong.

Why not get a bit more practice with some biology quizzes and then come back and have another try!
Select all that apply:
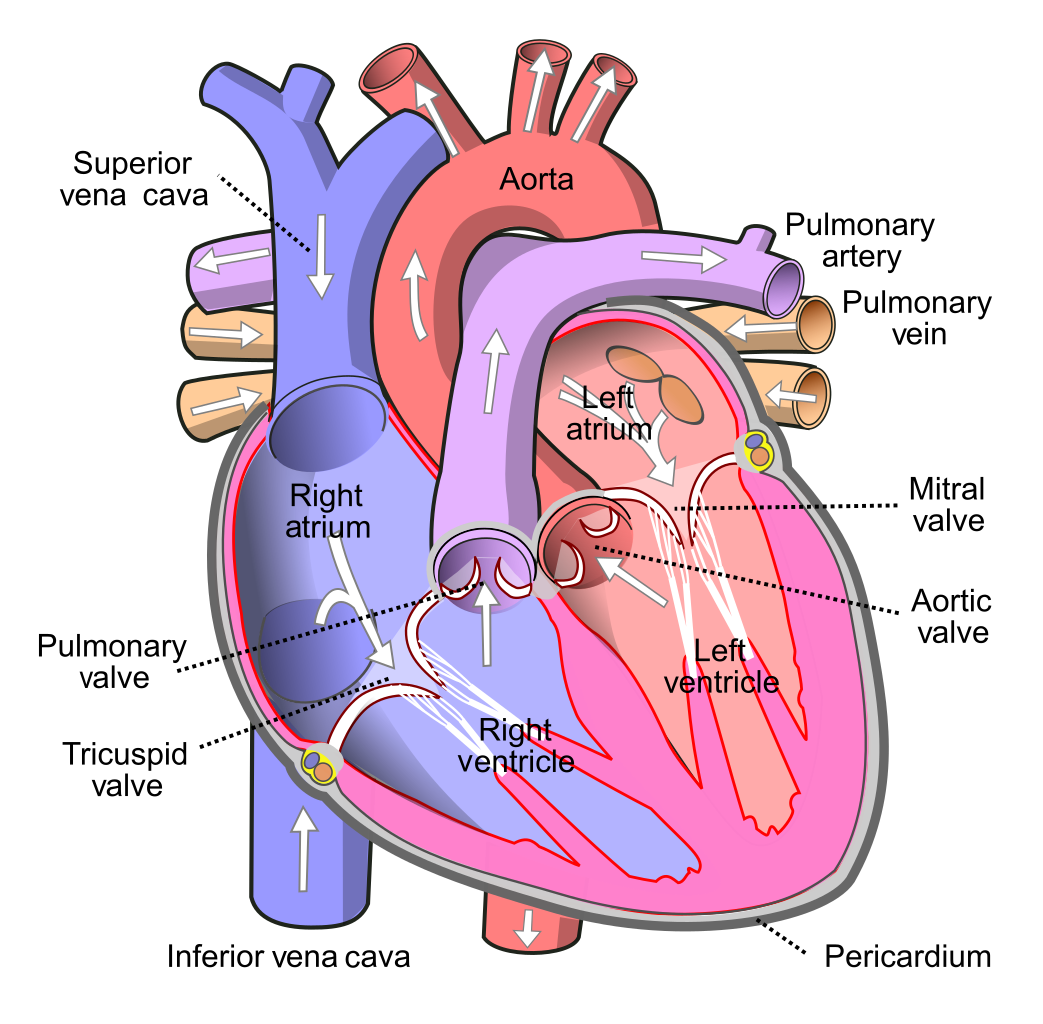
Select all that apply:
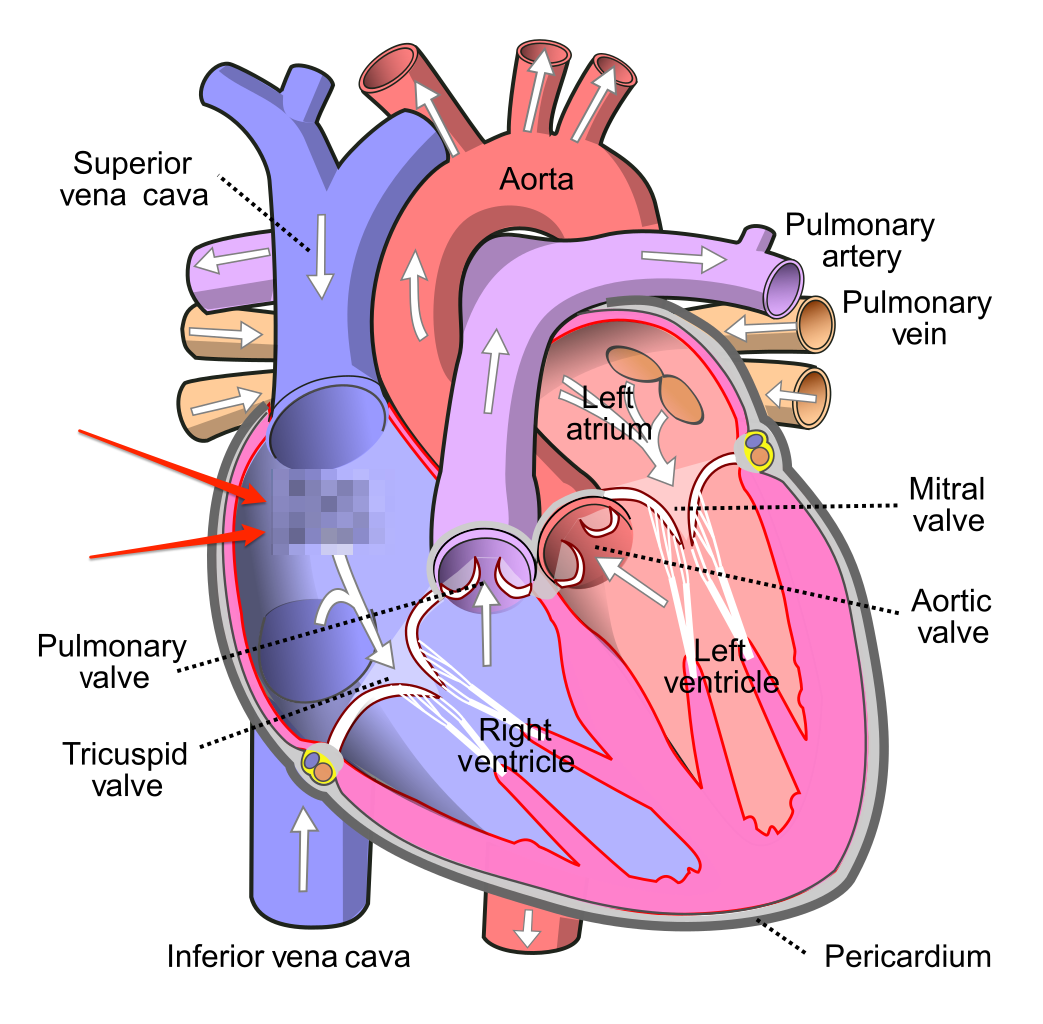
Select all that apply:
Select all that apply:
Select all that apply:
The blood vessels are constricted or dilated depending on where the blood flows.
The muscles required for running for example are dilated since they are required to match the “fight or flight” response. Others are constricted as they are temporarily deemed less important.
Select all that apply:
Select all that apply:
Select all that apply: