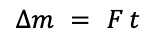Mock test. 100 marks available.
GCSE AQA Physics Paper 1
Good Luck!
Quiz Summary
0 of 55 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 55 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 6 Mark Questions 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 55
1. Question
2 point(s)[question number = 01.1] Use one of the following numbers to fill in the blank:
110, 12, 24, 230-
Complete the sentence: In the UK the domestic electricity supply has a frequency of Hz and is about V.
Correct 2 / 2 PointsIncorrect / 2 Points -
-
Question 2 of 55
2. Question
2 point(s)[question number = 01.2] Use one of the following numbers to fill in the blank:
Batteries, mains power, does, does not
-
Complete the sentence: Direct current is supplied by and charge change direction.
Correct 2 / 2 PointsIncorrect / 2 Points -
-
Question 3 of 55
3. Question
3 point(s)[question number = 01.3] A wire carries 15 A of current at 120 V. Calculate:
a) The power in watts
b) The resistance in ohms
c) The current that would flow if the voltage doubled but resistance stayed the same-
- watts
- ohms
- amperes
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 4 of 55
4. Question
3 point(s)[question number = 01.4] Drag and drop to match the purpose with the correct wire
Sort elements
- Live
- Earth
- Neutral
- Connects the appliance to the power supply
- Provides an alternative (low resistance) path for the current in the case of a fault
- Provides a return path to the power supply from the appliance
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 55
5. Question
6 point(s)[question number = 01.5] Students are told that they should investigate how the resistance of a wire changes with its length.
Plan an investigation to determine the relationship between the length of a wire and its resistance. (enter your answer)
You should include:
- how to set up the apparatus and the materials you would use:
- how to collect and record data
- how to ensure accuracy and reliability of results.
Correct 6 / 6 PointsIncorrect / 6 Points -
Question 6 of 55
6. Question
4 point(s)[question number = 01.6] A circuit contains a 12-volt battery connected to three resistors in series. Resistor 1 is 4 ohms, Resistor 2 is 6 ohms, and Resistor 3 is 2 ohms.
a) Calculate the total resistance in the circuit.
b) Using Ohm’s Law, calculate the current flowing through the circuit.
c) If the circuit runs for 5 minutes, calculate the total electrical energy consumed in joules.
d) Calculate the total power dissipated by all three resistors combined.
-
- Total resistance = ohms
- Current = ampere
- Total electrical energy consumed in 5 minutes = joules
- Total power dissipated = watts
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 7 of 55
7. Question
3 point(s)[question number = 02.1] Drag and drop to match the disadvantages to the correct energy resource
Sort elements
- Fossil fuels
- Wind and solar energy
- Tidal energy
- Produce greenhouse gases
- Intermittency
- Salt water is corrosive
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 55
8. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 02.2] Which of the following are fossil fuels?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 55
9. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 02.3] Match each outcome to the corresponding reaction type.
Sort elements
- Produces two smaller nuclei and neutrons
- Causes the explosion in nuclear weapons
- Nuclear Fission
- Uncontrolled Chain Reaction
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 55
10. Question
2 point(s)[question number = 02.4] Select all valid descriptions of nuclear fusion:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 55
11. Question
3 point(s)[question number = 02.5] Select all statements that accurately describe nuclear fission:
Correct 3 / 3 PointsIncorrect / 3 Points -
Question 12 of 55
12. Question
3 point(s)[question number = 02.6] Use some of the following answers to fill in the blanks:
Fusion, gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy, fission-
In nuclear , energy is released as , while nuclear converts mass into radiation energy.
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 13 of 55
13. Question
4 point(s)[question number = 02.7] Which of the following are reasons why hydroelectric dams are problematic?
Correct 4 / 4 PointsIncorrect / 4 Points -
Question 14 of 55
14. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 03.1] Convert 0.0000789 to standard form
- x 10
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 15 of 55
15. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 03.2] Convert 236,000 into standard form
- x 10
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 16 of 55
16. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 03.3] Convert 2400μm to m
-
m
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 17 of 55
17. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 03.4] Convert 32,400 s to hours
-
H
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 18 of 55
18. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 03.5] A square metal plate has sides of length 2.54 × 10⁵ micrometres. Calculate the perimeter of the plate in metres, give your answer in ordinary form to three decimal places.
-
m
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 19 of 55
19. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 04.1] Calculate the change in momentum of an object that experiences a force of 350 N over 15 s.

-
kg m/s
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 20 of 55
20. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 04.2] Calculate the distance moved when a 650 J of work is done to move a 160 N object. Leave your answer to 1 d.p.
-
m
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 21 of 55
21. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 04.3] Jack moves a cube weighing 250N. He moves the cube by 2.5m in a straight line. Calculate the work done by Jack.
-
J
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 22 of 55
22. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 04.4] A crane raises a concrete bucket 12m into the air. The bucket including the cement weighs 850N. Calculate the work done. Answer to 1d.p
-
J
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 23 of 55
23. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 05.1] A train is travelling at 45 miles per hour. The driver puts on the brakes in order to stop at the station. Where is the kinetic energy of the train being transferred to?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 55
24. Question
2 point(s)[question number = 05.2] Energy can be transferred to useful and non-useful forms. Which of the following are non-useful transfers of energy?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 55
25. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 05.3] How can you reduce the effect of friction in the chain on a bicycle?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 55
26. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 05.4] What are the units we use for measuring energy?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 55
27. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 05.5] What do we use to slow the rate of heat loss out of a house?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 55
28. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 05.6] Which process transfers heat using electromagnetic waves?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 55
29. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 05.7] Using the kinetic energy equation – calculate the kinetic energy of a car with a mass of 1200kg travelling at 10 m/s.
-
J
CorrectIncorrectHint
If you do not remember the kinetic energy equation visit the link above the quiz
-
-
Question 30 of 55
30. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 05.8] How is gravitational potential energy stored?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 55
31. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 05.9] An object with a mass of 5kg is 100m above the ground and has 35 J of gravitational potential energy. What will happen to the gravitational potential energy if the mass was increased to 10kg?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 55
32. Question
3 point(s)[question number = 06.1] Drag and drop to match the description to the type of particle
Sort elements
- Ions
- Alpha particle
- Beta particle
- Atoms which have gained or lost electrons
- A helium nucleus – two protons and two neutrons
- An electron
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 55
33. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 06.2] Which material do we commonly use to line the containers where radioactive sources are stored?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 55
34. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 06.3] The half-life of cobalt-60 is 5 years. If there are 100g of cobalt-60 in a sample, how much will be left after 15 years?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 55
35. Question
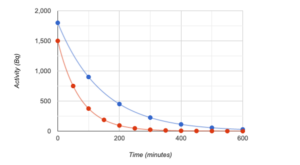
1 point(s)[question number = 06.4] The graph shows the activity of two different radioactive substances. Determine the half-life of Source B (red) in minutes.

-
minutes
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 36 of 55
36. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 06.5] Put the types of radiation in order from most ionising to least ionising.
- Beta particles
- Alpha particles
- Gamma rays
View Answers:
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 37 of 55
37. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 06.6] The graph shows the activity of two different radioactive substances. Determine the half-life of Source A (blue) in minutes. Do not add the units.

-
minutes
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 38 of 55
38. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 06.7] Ionising radiation can penetrate materials. Put the types of radiation in order from most penetrating to least penetrating.
- Gamma rays
- Alpha particles
- Beta particles
View Answers:
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 39 of 55
39. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 06.8] A GM tube is often connected to a counter that clicks each time radiation is detected. What do we call the number of clicks per second or minute?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 55
40. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 07.1] Calculate the specific latent heat of vaporisation/evaporation for carbon dioxide using the following information. You have a 1.5kg sample of carbon dioxide that changed state from a liquid to a gas. The energy required to evaporate it was 856.62 J
-
J/kg
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 41 of 55
41. Question
5 point(s)[question number = 07.2] Use some of the following words to complete the definition.
Specific, cool, leftover, latent, power, energy, 1, 100, 1000, mixture, state
-
Complete the definition:
- Specific describes the amount of it takes to make kg of a substance change .
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 42 of 55
42. Question
6 point(s)[question number = 07.3] Match the change of state with the transition using the words below.
Freezing, sublimation, evaporation or boiling, condensation, melting, deposition
-
- Gas to liquid =
- Liquid to solid =
- Solid to liquid =
- Liquid to gas =
- Solid to gas =
- Gas to solid =
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 43 of 55
43. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 07.4] Calculate the mass of a block of platinum when the change in thermal energy is 50 J, the specific heat capacity is 0.12 J/kg °C, and the change in temperature is 10 °C.
-
Kg
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 44 of 55
44. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 07.5] When a substance changes from a solid to a liquid, what happens to the mass?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 55
45. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 07.6] Why did Ernest Rutherford’s experiments with gold foil demonstrate that atoms consist of mostly empty space?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 46 of 55
46. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 07.7] Find the volume of a silver block that has a mass of 159g and a density of 10.49 g/cm³. Answer to 1 decimal place.
-
cm³
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 47 of 55
47. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 07.8] Calculate the density of a gold bar that has a mass of 25kg and a volume of 0.0013m³. Answer to 1 decimal place.
-
kg/m³
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 48 of 55
48. Question
3 point(s)[question number = 08.1] A metal cube has a mass of 648g and each side is 6 cm long. Calculate: a) The volume in m³ b) The density in kg/m³ c) The mass in kg of a second cube of the same material with 0.03 m sides
-
- m³
- kg/m³
- kg
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 49 of 55
49. Question
3 point(s)[question number = 08.2] An engineer wants to build a cube 5 times larger than the original cube (6 cm sides) using identical small metal cubes of the same size as the original. Calculate:
a) How many of the original-sized cubes would be needed to complete this larger cube?
b) What would be the total mass of this larger cube?
c) What would be the volume of the new cube?
-
- cubes
- kg
- m³
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 50 of 55
50. Question
5 point(s)[question number = 08.3] 2000 of the 5 times larger metal cubes (30 cm sides) need to be transported to a construction site within 3 days. A standard lorry flatbed has dimensions of 13.6 m length × 2.55 m width, with a maximum permitted height of 4.9 m. The maximum payload (carrying capacity) of each lorry is 28,000 kg. Calculate:
a) How many cubes can fit along the length and width of the flatbed? (Ignore height for now)
b) If these cubes can be stacked, how many layers high can they go within the legal height limit?
c) What is the total number of cubes that could be transported in one journey?
d) Given each cube weighs 81 kg, what is the actual maximum number of cubes that can be transported per journey due to the weight limit?
e) How many lorry journeys will be required?
-
- cubes
- layers
- cubes
- cubes per journey
- journeys
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 51 of 55
51. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 09.1] What is transferred between materials to create static electricity?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 52 of 55
52. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 09.2] Use some of the following answers to fill in the blanks:
Electrons, force, positive, repel, attract-
When two objects with the same charge are brought close together, they .
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 53 of 55
53. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 09.3] Which concept helps explain the non-contact force between charged objects?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 54 of 55
54. Question
2 point(s)[question number = 09.4] Use some of the following answers to fill in the blanks:
Stronger, weaker, closer, farther-
As two charged objects move , the force they exert on each other becomes .
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 55 of 55
55. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 09.5] Arrange the steps in the correct order to describe the production of static electricity through rubbing.
- One material gains a positive charge, the other a negative charge
- Rubbing two insulating materials together
- Electrons transfer from one material to another
View Answers:
CorrectIncorrect -
Is this higher or foundation?
This is a combined paper for higher and foundation students. You can achieve grades 1 – 9 on this paper, so it is suitable for all. Grades are moderated against the average result to give the most accurate indication of your performance. You can look at – How is this paper marked? for more information.
How is this paper marked?
This paper is automatically marked to determine which questions were answered correctly.
Your grade is determined using a Z-Score moderation system. Your GCSE exams are also moderated comparably so that the difficulty of papers is taken into account.
Roughly, this works by calculating your overall percentage and comparing it to the average percentage and the standard deviation. This means that for harder papers you need fewer points to get the same grade as you would for an easier paper.
As more students attempt the paper, the average score and standard deviation more accurately represent the difficulty of the paper and the grades become more accurate.
Making these papers and the marking system took considerable effort so if you found them helpful for your revision, please show your appreciation by rating the page.
Related Quizzes
Which exam board are you studying?