Mock test. 70 marks available.
GCSE AQA Combined Science Trilogy Physics Paper 2
Good Luck!
Quiz Summary
0 of 38 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 38 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 6 Mark Questions 0%
- Physics 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 38
1. Question
4 point(s)[question number = 01.1] Drag and drop to match the quantity with the example
Sort elements
- Scalar
- Vector
- Speed
- Momentum
-
Mass
-
Weight
-
Scalar
-
Vector
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 38
2. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 01.2] Drag and drop to match the description to the type of quantity
Sort elements
- Vectors
- Scalars
-
Have both magnitude and direction
-
Only have magnitude
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 38
3. Question
4 point(s)[question number = 01.3] Drag and drop to match the quantity with the correct type
Sort elements
- Vector
- Scalar
- Energy
- Velocity
-
Acceleration
-
Distance
-
Scalar
-
Vector
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 38
4. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 02.1] If a car experiences a resultant force in the forwards direction, what will happen to the motion of the car?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 38
5. Question
3 point(s)[question number = 02.2] Drag and drop to match the description to the Law of Motion
Sort elements
- Newton's 1st Law
- Newton's 2nd Law
- Newton's 3rd Law
-
Objects in motion stay in motion and objects at rest stay at rest (unless acted upon by a resultant force)
-
F = MA (resultant force = mass x acceleration
-
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 38
6. Question
2 point(s)[question number = 02.3]
-
Complete the equation for resultant force (Newton’s Second Law). Force = x
Correct 2 / 2 PointsIncorrect / 2 Points -
-
Question 7 of 38
7. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 02.4] In an equilibrium situation – the forces between two objects are?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 38
8. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 02.5] Calculate the force of a ball with a mass of 15kg that is accelerated at 2m/s²?
-
N
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 9 of 38
9. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 03.1] Calculate the mass of a vehicle with a momentum of 42000 kg m/s and a velocity of 25 m/s.
-
kg
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 10 of 38
10. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 03.2] Calculate the force when an object changes its momentum by 2550 kg m/s in 5 seconds.
-
N
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 11 of 38
11. Question
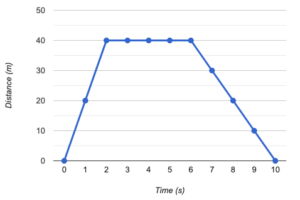
1 point(s)[question number = 04.1] Determine the speed of the object between 0 and 2 seconds.
-

m/s
CorrectIncorrectHint
answer to 2 decimal places
calculate the gradient.
-
-
Question 12 of 38
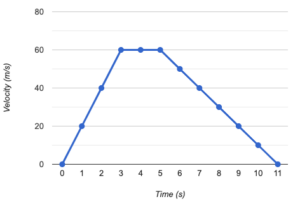
12. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 04.2] Calculate the distance travelled by the runner in the velocity/time graph.
-

m
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 13 of 38
13. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 04.3] What is happening to the speed of the object in the graph between 0 and 7 seconds?
Use one of the following options: Accelerating, decelerating, no change in velocity.CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 14 of 38
14. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 04.4] What is the acceleration of an object that has an initial velocity of 10m/s and a final velocity of 50m/s. The object took 15s to accelerate to the final velocity.
CorrectIncorrectHint
Use the following equation:
a = (v − u)
t
-
Question 15 of 38
15. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 04.5] Calculate the acceleration of an object with the following characteristics. Final velocity = 50m/s, Initial velocity 0m/s, Distance travelled = 350m
-
m/s²
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 16 of 38
16. Question
2 point(s)[question number = 05.1]
-
Force exerted on a spring = x
Correct 2 / 2 PointsIncorrect / 2 Points -
-
Question 17 of 38
17. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 05.2] Calculate the spring constant for a spring with an extension of 25mm and a force exerted of 1.6 N
-
N/m
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 18 of 38
18. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 05.3] Calculate the force exerted on a spring with an extension of 40cm and a spring constant of 12.5 N/m (Equation)
-
N
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 19 of 38
19. Question
6 point(s)[question number = 05.4] Students in a physics class have been learning about Hooke’s Law and want to learn more.
Plan an investigation to determine the relationship between the force applied to a spring and its extension. (enter your answer)
You should include:
- how to set up the apparatus and the materials you would use
- how to collect and record data
- how to ensure accuracy and reliability of results.
Correct 6 / 6 PointsIncorrect / 6 Points -
Question 20 of 38
20. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 06.1] Which of these is an example of transverse waves?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 38
21. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 06.2] What happens to the speed of light waves when they go from air to water?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 38
22. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 06.3] Which layer of the Earth’s atmosphere absorbs ultraviolet light?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 38
23. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 06.4] What do we call the boundary between two different mediums?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 38
24. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 06.5] Place the types of electromagnetic radiation in order from longest wavelength to shortest wavelength
-
Infrared waves
-
Microwaves
-
X rays
-
Radio waves
-
Gamma rays
-
Visible light
-
Ultraviolet
View Answers:
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 25 of 38
25. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 06.6] No refraction takes place if a wave is travelling along which line?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 38
26. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 06.7] What kind of waves are electromagnetic waves?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 38
27. Question
4 point(s)[question number = 06.8] Drag and drop to match the wave to the correct type
Sort elements
- Transverse
- Electromagnetic waves
- Longitudinal
- Sound waves
-
Guitar string vibrations
-
Transverse
-
Seismic P waves
-
Longitudinal
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 38
28. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 07.1] What devices are used to determine the shape of a magnetic field around a bar magnet?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 38
29. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 07.2] Where are magnetic forces strongest?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 38
30. Question
3 point(s)[question number = 07.3] Which of the following are uses for magnets?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 38
31. Question
4 point(s)[question number = 07.4] Which of the following metals are magnetic?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 38
32. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 07.5] Use one of the following words to fill in the blank:
Volcanic, magnetic, compression, refraction-
Fill in the blank: A current flowing through a wire causes a field.
CorrectIncorrectHint
Use one of the following words:
magnetic
volcanic
electric
solar
-
-
Question 33 of 38
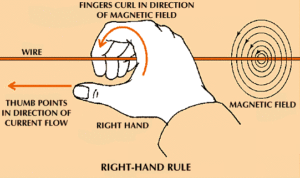
33. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 07.6] This diagram shows the direction of a magnetic field caused by a current flowing through a conductor. Where is the magnetic field strongest?
(a – closest to the wire) (b – further away from the wire) (c – at a middle distance from the wire)-

Enter the letter of your choice from the options above the image.
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 34 of 38
34. Question
2 point(s)[question number = 07.7] Which of the following are ways that a magnetic field of an electromagnet can be made stronger?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 38
35. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 07.8] What is the force acting on a conductor carrying current at right angles to a magnetic field when: magnetic flux density = 0.005 T , current = 3 A and length of wire = 150m?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 38
36. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 08.1] Convert 6.5 x 10⁴ to ordinary form
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 38
37. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 08.2] Convert 42,000 to standard form
-
x 10
CorrectIncorrect -
-
Question 38 of 38
38. Question
1 point(s)[question number = 08.3] Convert 59 cm to km
-
km
CorrectIncorrect -
Is this higher or foundation?
This is a combined paper for higher and foundation students. You can achieve grades 1 – 9 on this paper, so it is suitable for all. Grades are moderated against the average result to give the most accurate indication of your performance. You can look at – How is this paper marked? for more information.
How is this paper marked?
This paper is automatically marked to determine which questions were answered correctly.
Your grade is determined using a Z-Score moderation system. Your GCSE exams are also moderated comparably so that the difficulty of papers is taken into account.
Roughly, this works by calculating your overall percentage and comparing it to the average percentage and the standard deviation. This means that for harder papers you need fewer points to get the same grade as you would for an easier paper.
As more students attempt the paper, the average score and standard deviation more accurately represent the difficulty of the paper and the grades become more accurate.
Making these papers and the marking system took considerable effort so if you found them helpful for your revision, please show your appreciation by rating the page.
Related Quizzes
Which exam board are you studying?