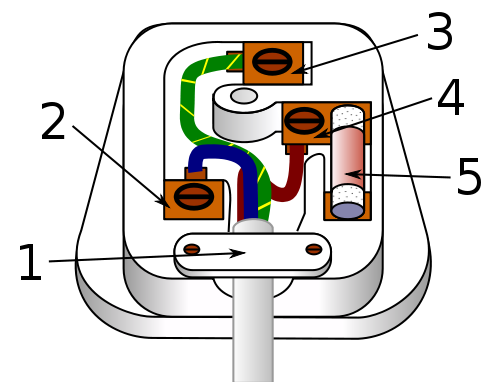
If a switch is turned on then the current will flow along the live wire, around the circuit (including over any appliances/components) and then it will return via the neutral wire.
The potential difference of the live wire is 230V, whilst the neutral wire is 0V if correctly connected. This difference allows a current to flow only in a single direction. If a fault develops, where the live wire touches the metal casing of an appliance, the earth wire will receive the current instead, should you touch the casing.
The earth wire has a very low resistance, which is lower than the human body and so the current flows through the earth instead of through you. Then this will cause a very large current to flow through the earth wire and fuse, causing the fuse to “blow” or melt, breaking the circuit.
Circuit breakers act in the same way as fuses except they can be reset without replacing them. This makes them multi-use. Check out our quiz on the function of components.